
On the Design tab, in the Controls group, click Text Box. However, Access does not enable rich text editing when you manually add a control to a form or report, even if you subsequently bind that control to a Long Text field with rich text formatting. If you have data in the Long Text field of your table, that data appears in the text control on your form or report.
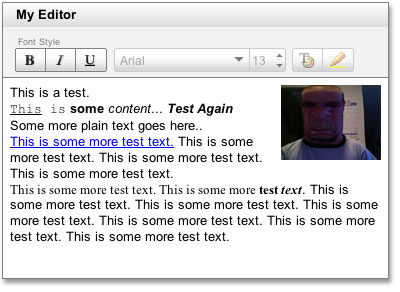
If you use the commands on the Create tab to create a form or report, and you have enabled rich-text editing for the underlying Long Text field, the resulting text box control inherits the Text Format property set for the Long Text field. Top of Page Enable rich text formatting for form and report controls Select the Long Text field that you want to change, and in the lower part of the table designer, on the General tab, scroll down to the Append Only property.Ĭlick the field next to the property and select No from the list. Otherwise, Access hides the text in the field whenever you place your cursor in that field, or in any form or report controls bound to that field. To enable rich text formatting for a field, ensure that the Append Only property for the field is disabled. Top of Page Clear the Append Only property After you have applied the change to plain text and the table has been saved, you cannot undo the change.Ĭlick in the TextFormat box and select Plain Text. Important When you change a field from rich text to plain text, Access prompts you with a warning that all formatting will be removed. Top of Page Change a rich text field to plain text
In the table design grid, click the Long Text field that you want to change to rich text.Ĭlick the Text Format box and select Rich Text. Open the table that contains the field in Design View. Under Field Properties, click the General tab.Ĭlick inside the Text Format box and select Rich Text. In the Data Type column, select Long Text. Then, in the Field Name column, type a field name. In the table design grid, locate the first empty row. Select Click to Add, and then select Long Text from the list.ĭouble click the field header and enter a meaningful name for the new field. You can create a rich text field in table Datasheet View or Design View. Makes text look like it was marked with a highlighter pen. The number appears prior to each paragraph.īegins placing a bullet before each paragraph. If the text is already underlined, removes the underline.Īligns the text against the right margin.īegins numbering paragraphs. If the text is already italic, removes the italic. If the text is already bold, removes the bold. The following table shows supported rich text formatting options: However, you can change the TextFormat property on the text box control. The text box control has a TextFormat property that inherits its initial value from the TextFormat property of the Long Text field. After you store rich text in a Long Text field, you can display it in a form or report by using a text box control. You set the TextFormat property for the Long Text field in table in Datasheet View and Design View. PlainText Enables plain text and is interpreted as plain text. RichText Enables rich text and is stored and interpreted as rich HTML markup. To create a field for storing rich text, you create a Long Text field and then set that field's TextFormat property to RichText.
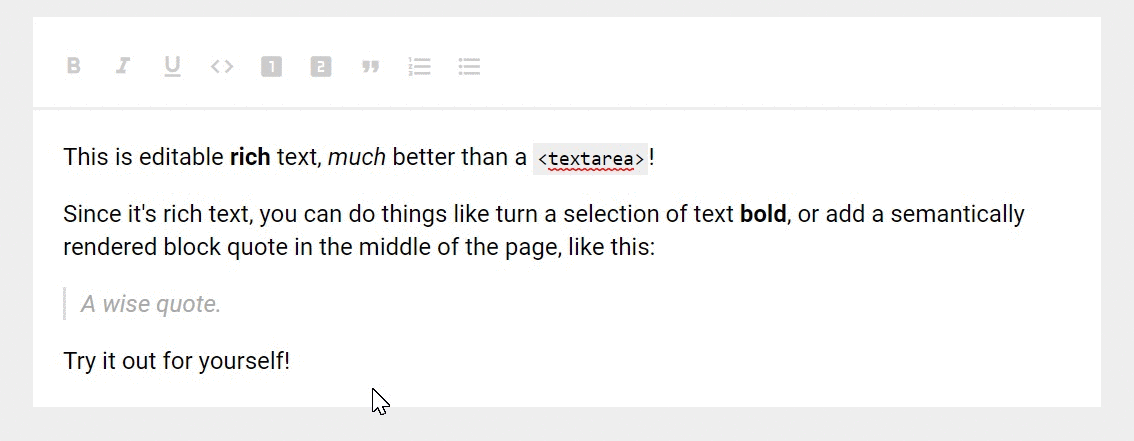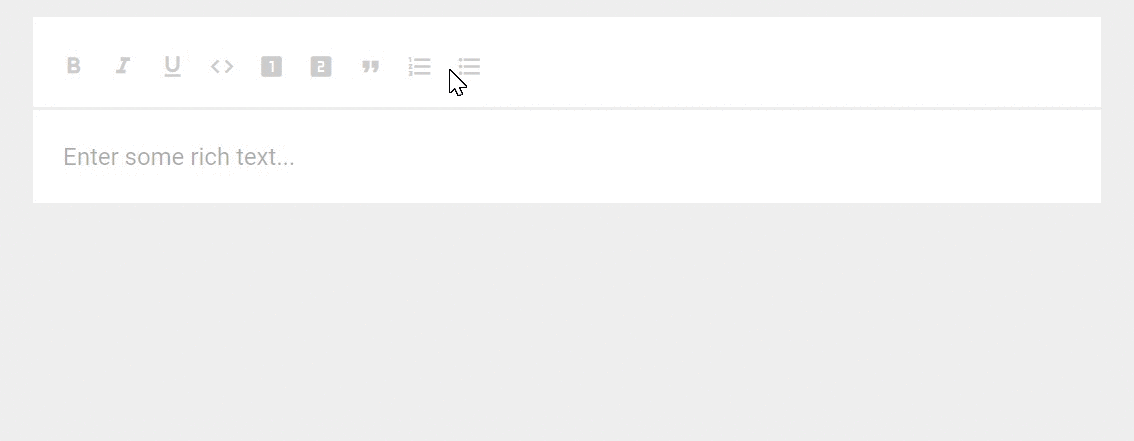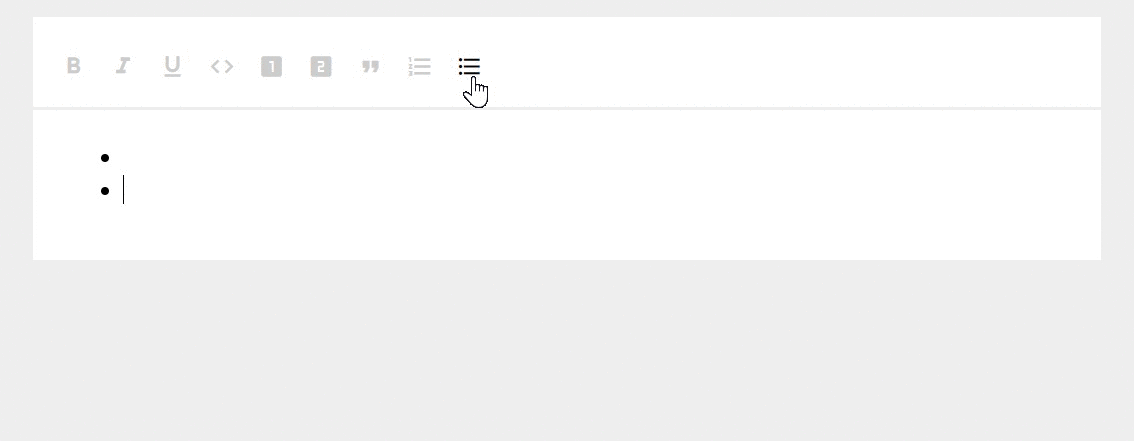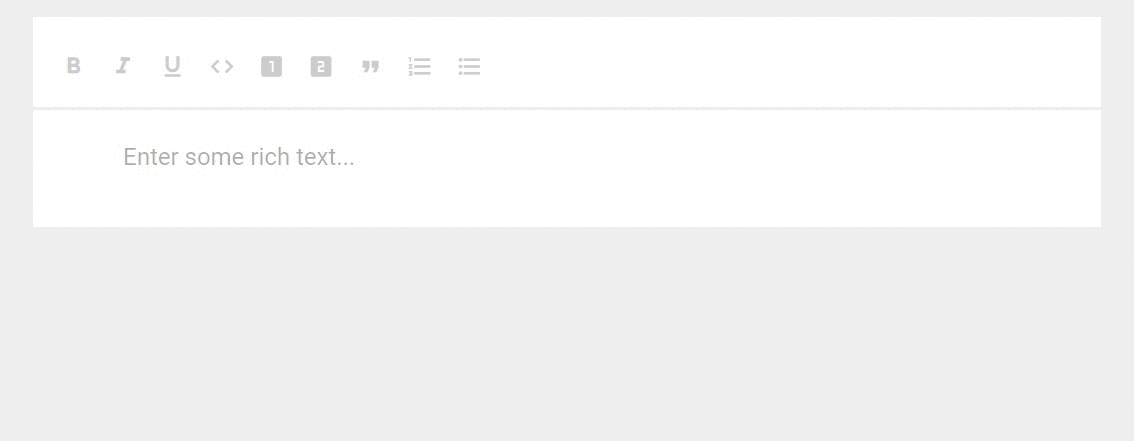
Access uses HTML because it provides a greater degree of compatibility with rich-text fields stored in SharePoint lists.Īccess stores rich text by using the Long Text data type, which is the only data type that has built-in support for rich text.
#Rich text example code#
Behind the scenes, Access applies Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) formatting code to your data.
You format your data by using common formatting tools, such as the Ribbon and the Mini Toolbar. Rich text is text that is formatted with common formatting options, such as bold and italics, that are unavailable with plain text. In this articleĮnable rich text formatting for form and report controls You can apply formatting to all or part of the contents of the field when the field is displayed in a datasheet and by editing the field through a bound control in a form or report. For example, you can make the text bold or underlined, apply different fonts to individual words or characters, and change text colors. You can store rich, formatted text in an Access database by using a Long Text (also called Memo) field and setting the field's TextFormat property to RichText. Access for Microsoft 365 Access 2021 Access 2019 Access 2016 Access 2013 Access 2010 Access 2007 More.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
